Scope of Biochemistry:
The scope of biochemistry is broad and encompasses a wide range of topics and applications. Here are some key aspects of the scope of biochemistry:
1. Biomolecules: Biochemistry explores the structure, function, and interactions of biomolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), lipids, carbohydrates, and small molecules like vitamins and hormones. Understanding these molecules is fundamental to unraveling the complexities of life processes.
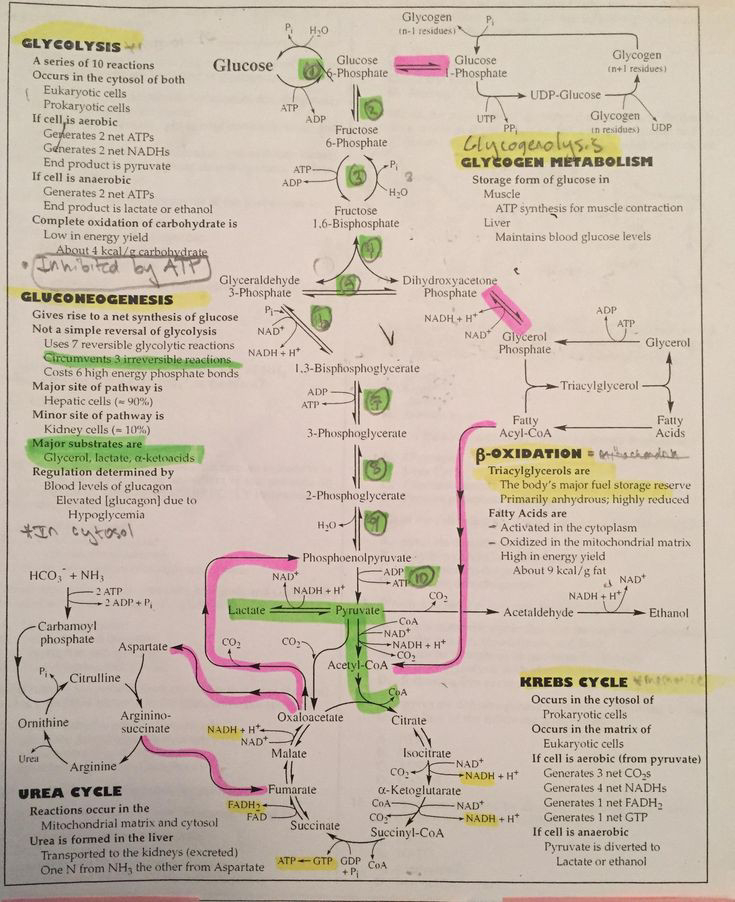
2. Metabolism: Biochemistry delves into the metabolic pathways that occur in cells and organisms. This includes processes like glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, which are essential for energy production and the synthesis of biomolecules.
3. Enzymes: Biochemists study enzymes, which are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in living systems. Enzymes play a critical role in regulating cellular processes and are vital for maintaining homeostasis.
4. Genetics: Biochemistry intersects with genetics through the study of molecular genetics and genomics. It examines how genes are transcribed and translated to produce proteins, as well as how genetic mutations can lead to diseases.
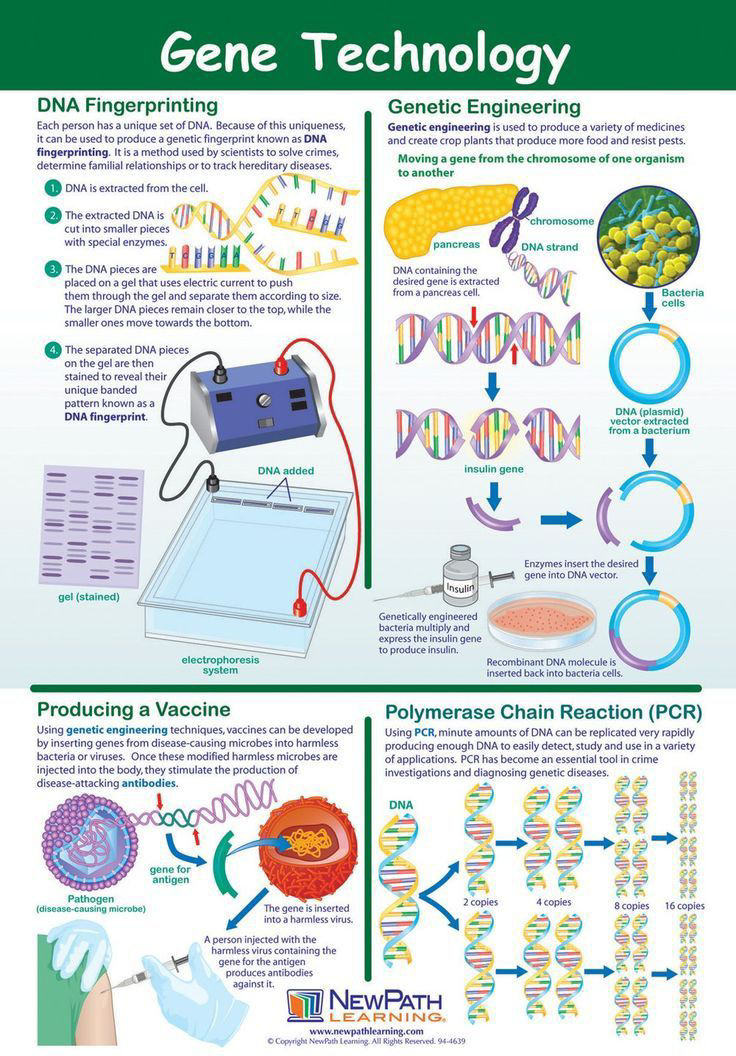
5. Biotechnology: Biochemistry has a significant impact on biotechnology and genetic engineering. It is involved in the development of recombinant DNA technology, the production of biopharmaceuticals, and the manipulation of genes for various applications.
6. Medicine: Biochemistry is essential in the field of medicine. It helps in understanding the molecular basis of diseases, designing drug therapies, and diagnosing illnesses through techniques like molecular diagnostics.
7. Nutrition: Biochemistry contributes to our understanding of nutrition by studying how the body processes and utilizes nutrients, leading to insights into dietary requirements and health.
8. Environmental Science: Biochemistry is relevant to environmental science as it can help in the study of microbial processes involved in bioremediation, the breakdown of pollutants, and understanding the impact of chemicals on ecosystems.
9. Agriculture: Biochemistry plays a role in improving crop yield and quality by studying plant metabolism, nutrient uptake, and the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for agriculture.
10. Evolutionary Biology: Biochemistry provides insights into the evolution of life on Earth by examining the conservation and divergence of molecular processes across species.
In summary, biochemistry is a multidisciplinary field that investigates the chemical foundations of life. Its scope is vast and encompasses various aspects of biology, chemistry, and their applications, making it a crucial discipline for advancing our understanding of living organisms and improving our quality of life through medical, biotechnological, and environmental advancements.










No comments:
Post a Comment